Atmanirbhar Spending Surge
The Ministry of Defence announced a major capital contracting milestone on 30 December 2025, signing deals worth ₹1.82 trillion for the 2025-26 fiscal year. The expenditure reflects the Atmanirbhar Bharat mandate, prioritising indigenous missile systems and light helicopters. This aggressive procurement cycle is aimed at accelerating the transition away from legacy Soviet-origin hardware while sustaining the domestic defence industrial base.
Hypersonic Milestone
DRDO conducted a successful long-duration ground test of an actively cooled scramjet engine on 9 January 2026, sustaining operation for over 12 minutes. The milestone validates a critical propulsion technology for India’s indigenous Hypersonic Cruise Missile programme. By demonstrating stable combustion over an extended duration, the test places India among a small group of countries with the technological capability to develop hypersonic weapon systems operating at speeds above Mach 5.
Rocket-Missile Force Plan
Army Chief General Upendra Dwivedi said on 13 January 2026 that India is exploring plans to raise a dedicated “rocket-cum-missile force” in view of the evolving regional security situation, as both China and Pakistan have similar units. The proposal aims to consolidate long-range rockets and missiles currently distributed across existing units and enhance coordinated precision-strike capabilities, reflecting a doctrinal emphasis on long-range firepower and deterrence.
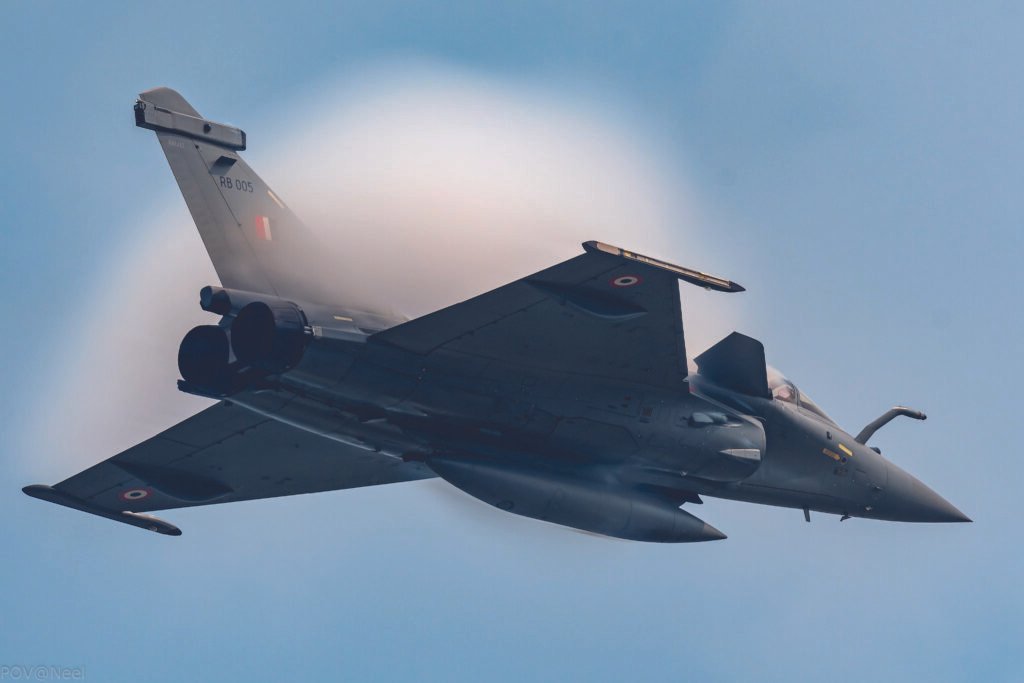
Sky-High Procurement
The Defence Procurement Board granted initial approval on 16 January 2026 for the acquisition of 114 Rafale fighter aircraft under the Multi-Role Fighter Aircraft project. The proposal now moves to the Defence Acquisition Council and then the Cabinet Committee on Security for final clearance. The planned procurement aims to bolster the Indian Air Force’s combat strength, which has fallen to 29 squadrons, and envisages most aircraft being manufactured in India with significant indigenous content.
Berlin’s India Roadmap
German Chancellor Friedrich Merz visited India on 12–13 January 2026 on his first official trip to the country. Leaders signed a Joint Declaration of Intent on a Defence Industrial Cooperation Roadmap to enhance long-term defence partnerships and technology collaboration. Germany also pledged €1.24 billion under its Green and Sustainable Development Partnership for renewable energy and climate-resilient projects and announced a visa-free transit facility for Indian passport holders, reflecting a broad deepening of bilateral ties.
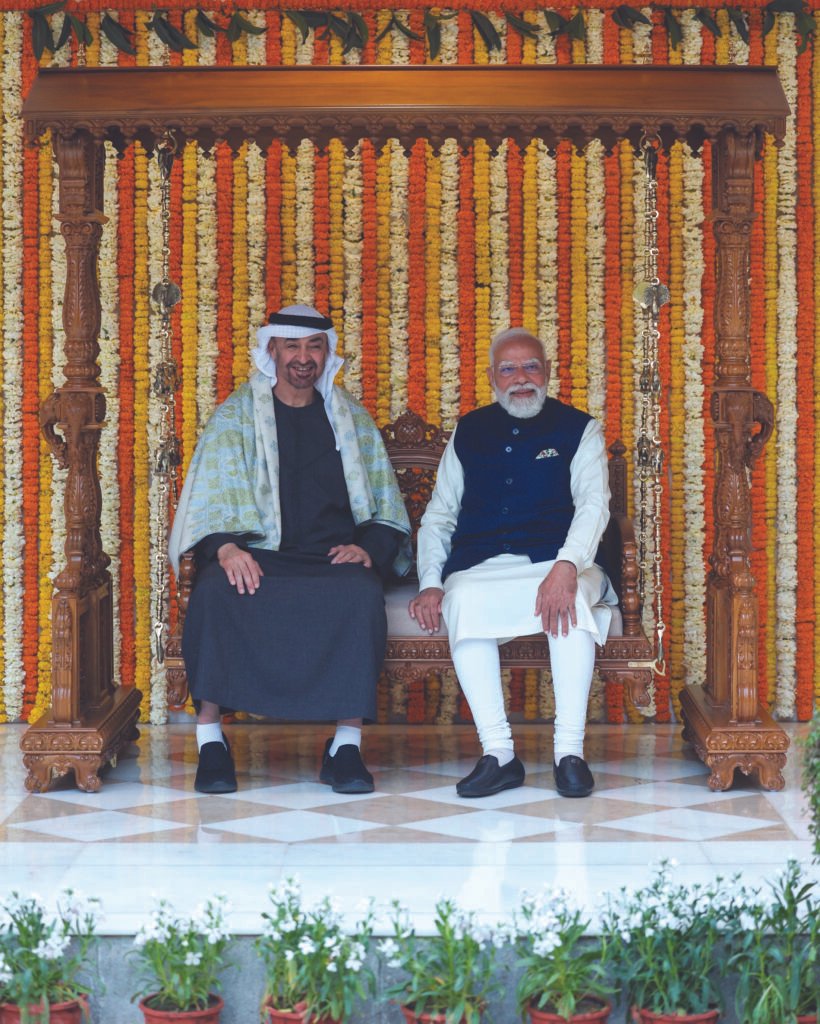

India, UAE Deepen Strategic Partnership
UAE President Sheikh Mohamed bin Zayed Al Nahyan visited New Delhi on 19 January 2026 at the invitation of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, underscoring continued momentum in the India–UAE Comprehensive Strategic Partnership. The leaders agreed to pursue a target of doubling bilateral trade to $200 billion by 2032, reaffirmed cooperation across strategic sectors, and signed a Letter of Intent on a Strategic Defence Partnership, signalling deeper defence cooperation and mutual security engagement. They also endorsed initiatives to strengthen trade, investment, space, technology, financial connectivity, and people-to-people ties.
Strategic Outreach
External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar spoke with U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio on 13 January 2026. Discussions covered civil nuclear cooperation following India’s new nuclear energy legislation, critical mineral supply chains, and energy security. The two also reviewed ongoing bilateral trade negotiations and exchanged views on regional developments, reaffirming support for a free and open Indo-Pacific.
Japanese Tech Export
The 18th India–Japan Strategic Dialogue was held on 16 January 2026 in New Delhi between EAM S. Jaishankar and Japanese FM Toshimitsu Motegi. Both sides launched a Japan–India AI Dialogue and agreed to convene a Joint Working Group on critical minerals to enhance cooperation on rare earths and supply chains. Discussions also covered defence cooperation, including ongoing talks on the Unified Complex Radio Antennae (UNICORN) system for Indian naval vessels.
India–Greece Defence Dialogue
India and Greece held their inaugural Joint Services Staff Talks in New Delhi on 12–13 January 2026. Co-chaired by senior officials from India’s Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff and the Hellenic National Defence General Staff, the talks established a tri-service framework to deepen military-to-military cooperation. Discussions focused on exchange programmes, capability development, and practical measures to strengthen operational engagement, while reviewing ongoing defence initiatives and identifying new areas for cooperation.
India–EU Trilateral Framework
India and the European Union held the first meeting of the Joint Steering Committee for India–EU trilateral cooperation in New Delhi on 21 January 2026. Co-chaired by EU Ambassador to India Hervé Delphin and MEA Joint Secretary Priyanka Chauhan, the meeting agreed on modalities for joint development cooperation with partner countries. The framework is anchored in shared values, mutual interests, and common developmental priorities, and provides a collaborative mechanism for implementing development projects in identified sectors and regions.
CCP Dialogue Push
A High-level Communist Party of China (CCP) delegation led by Sun Haiyan, Vice Minister of the CPC’s International Department, visited India from 12–14 January 2026. In New Delhi, the delegation met Foreign Secretary Vikram Misri to discuss business- and people-centric engagements and ways to advance bilateral ties. The group also held talks with political parties in India, including a meeting at the BJP headquarters, marking the first such party-to-party engagement since tensions following the 2020 Galwan Valley clash.
The PLI Efficiency Visa
The Indian government introduced the e-B-4 (e-Production Investment Business) visa in January 2026 to facilitate the entry of Chinese technical and business personnel required for production- and investment-linked activities in India, including projects under the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) framework. The digitally processed visa allows limited, purpose-specific travel for activities such as equipment installation, commissioning, quality checks, and production support, addressing operational disruptions faced by Indian manufacturers due to earlier visa constraints. The measure enables functional engagement while India continues to withhold formal diplomatic concessions and retains regulatory and security oversight.
Afghan Mission in Delhi
Mufti Noor Ahmad Noor was appointed Chargé d’affaires of the Embassy of Afghanistan in New Delhi by the Taliban in early January 2026. His role enables consular coordination and trade facilitation between Kabul and India, while India has not granted formal diplomatic recognition to the Taliban administration. This arrangement provides a practical channel for engagement on regional security and bilateral issues without extending official recognition.
India at Khaleda Zia’s Funeral
External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar attended the funeral of former Bangladesh Prime Minister Khaleda Zia in Dhaka on 31 December 2025. The visit signalled a calibrated shift in India’s ‘Neighbourhood First’ policy, demonstrating an intent to engage the full political spectrum following the recent leadership transition. This diplomatic agility is aimed at preventing a strategic vacuum and ensuring regional stability.

Nuclear CBMs Held Firm
India and Pakistan exchanged lists of nuclear installations and facilities on 1 January 2026, continuing a confidence-building measure in place since 1992 under their bilateral nuclear agreement. The annual exchange persists despite the absence of broader diplomatic engagement and remains one of the few functional risk-reduction mechanisms between the two sides. On the same day, both countries also exchanged lists of civilian prisoners and fishermen held in each other’s custody under the 2008 Consular Access Agreement.
Leading Diamond Traceability
India assumed the chair of the Kimberley Process for 2026 on 1 January. As a global hub for diamond cutting and polishing, New Delhi will prioritise digital certification and traceability to strengthen compliance and exclude conflict diamonds from legitimate supply chains. India’s leadership aims to reinforce transparency, governance standards, and global confidence in the diamond trade.
BRICS 2026
India formally launched its 2026 BRICS chairship on 13 January 2026, with External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar unveiling the official logo, theme, and website. The chairship’s theme, “Building for Resilience, Innovation, Cooperation and Sustainability,” reflects a people-centric approach to cooperation among BRICS members, prioritising practical collaboration and dialogue on global governance.
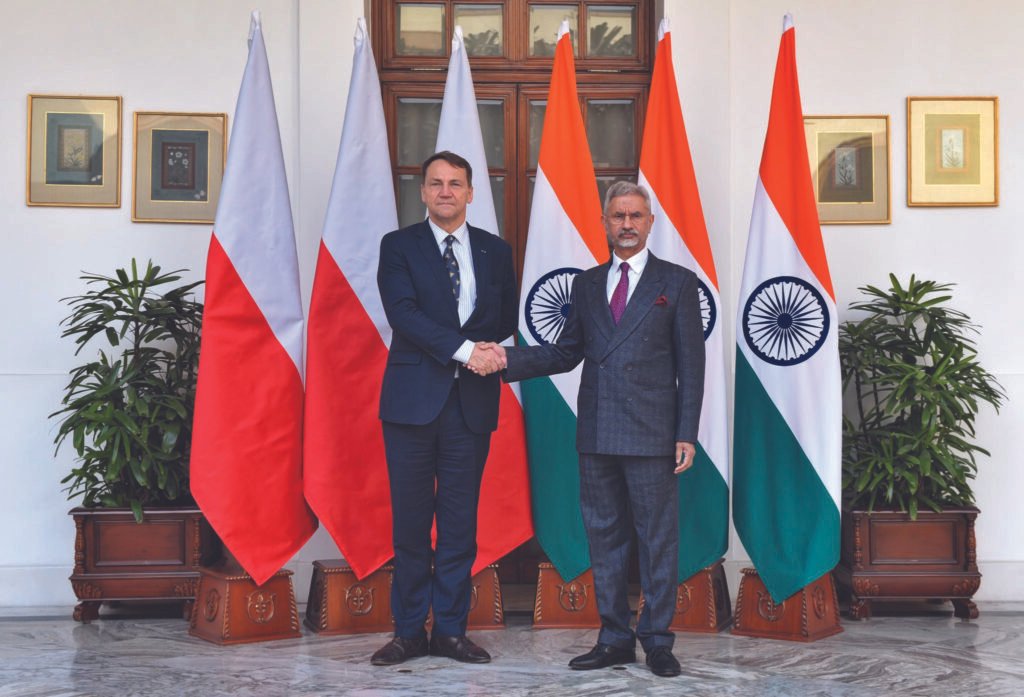
Calling Out Hypocrisy
External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar met Poland’s Deputy Prime Minister and Foreign Minister Radosław Sikorski in New Delhi on 19 January 2026. India flagged what it described as unfair and selective criticism of its energy and diplomatic ties with Russia amid the Ukraine conflict. Jaishankar also raised security concerns, urging Poland to adopt a zero-tolerance approach to terrorism and cautioning against actions that could fuel terrorist infrastructure in India’s neighbourhood, in the context of Poland’s recent engagement with Pakistan.

Digital Dharma
The 2nd Global Buddhist Summit was held in New Delhi on 24–25 January 2026 under the theme “Collective Wisdom, United Voice, and Mutual Coexistence.” Organised by the International Buddhist Confederation in collaboration with India’s Ministry of Culture, the summit brought together around 200 delegates and more than 800 participants from across the world to explore how Buddhist principles can inform responses to contemporary global challenges. A key feature of the event was the live demonstration of NORBU, an AI language model designed to engage younger audiences with Buddhist teachings.

